Study of The Organic Solar Cells Based on An Emeraldine Salt of Conductive Polyaniline
Amer N. Al-Daghman
Abstract
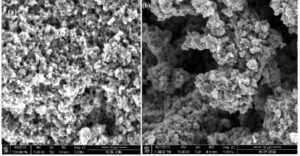
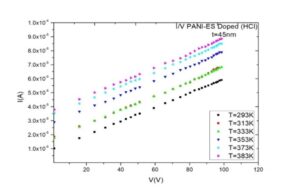
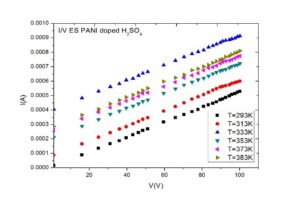
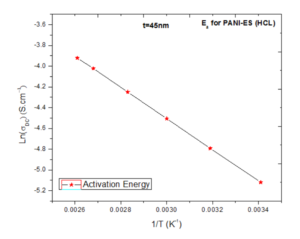
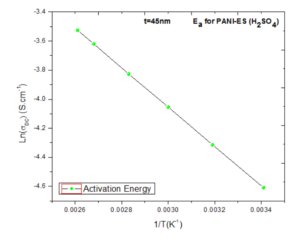
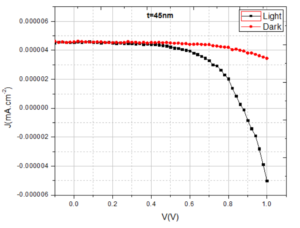
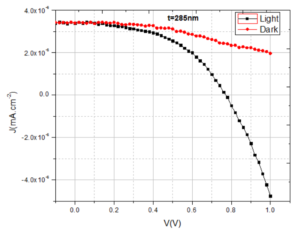
Conductive polymer of Polyaniline is synthesized by doping with inorganic and organic acids, namely Hydrochloric acid (HCl) and Sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Thin film quality depended on the method of chemical polymerization. The electrical conductivity of these films was measured by two probe methods. The direct current (DC) conductivities (σDC) are found to be about 1.2×10-4 S/cm and 2.98×10-4 S/cm for PANI (HCl) and PANI (H2SO4), respectively. The electrical conductivity is influenced by preparation conduction such as concentration of the ionic salted acid HCl, H2SO4 and temperature. The best electrical conductivity about 2.98×10-4 S/cm was found at 383K. Conductive σDC is measured down to a temperature of ~100 K and the apparent change in the activation energies Ea are found to be 0.124 eV, and 0.112 eV for PANI-HCl, and H2SO4 doping respectively. Conductivity σDC is less temperature dependent near room temperature, further decrease in temperature the σDC is strongly dependent. In material characterization, successful doping is corroborated by FESEM study. PANI (H2SO4) exhibited highest conductivity followed by PANI (HCl). Polyaniline is one of imported polymers for solar cells.
Keywords
emeraldine-salt; protonic acids; electric conductivity; organic solar cells
Cite This Article
Al-Daghman, A. N. (2022). Study of The Organic Solar Cells Based on An Emeraldine Salt of Conductive Polyaniline. International Journal of Scientific Advances (IJSCIA), Volume 3| Issue 2: Mar-Apr 2022, Pages 223-226, URL: https://www.ijscia.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Volume3-Issue2-Mar-Apr-No.244-223-226.pdf
Volume 3 | Issue 2: Mar-Apr 2022